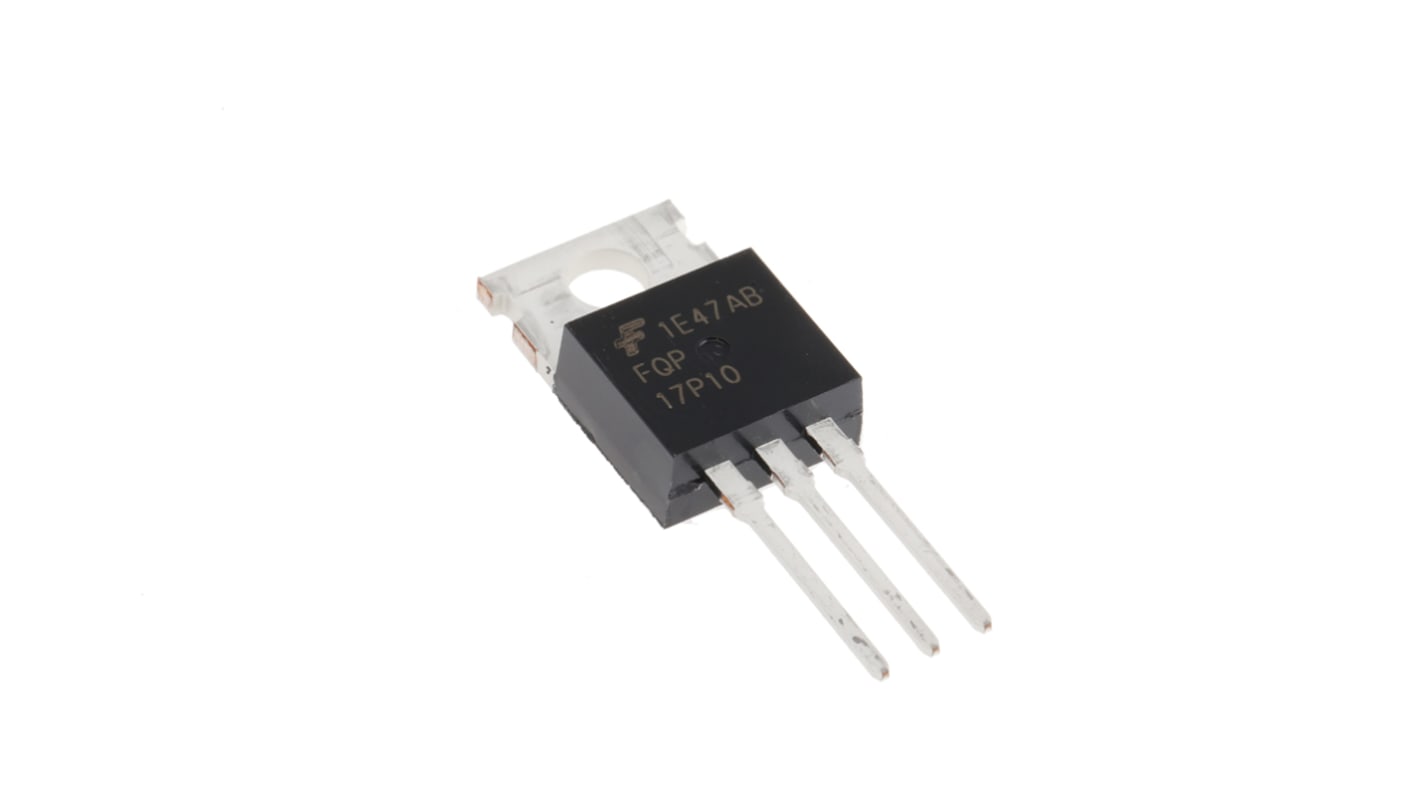
onsemi MOSFET FQP17P10
- N° de stock RS:
- 145-4520
- Référence fabricant:
- FQP17P10
- Fabricant:
- onsemi
Actuellement indisponible
Nous ne savons pas si cet article sera de nouveau disponible. RS a l'intention de le retirer de son assortiment sous peu.
- N° de stock RS:
- 145-4520
- Référence fabricant:
- FQP17P10
- Fabricant:
- onsemi
Spécifications
Documentation technique
Législations et de normes
Détails du produit
Recherchez des produits similaires en sélectionnant un ou plusieurs attributs.
Sélectionner tout | Attribut | Valeur |
|---|---|---|
| Marque | onsemi | |
| Product Type | MOSFET | |
| Sélectionner tout | ||
|---|---|---|
Marque onsemi | ||
Product Type MOSFET | ||
QFET® P-Channel MOSFET, Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor’s new QFET® Planar MOSFETs use advanced, proprietary technology to offer best-in-class operating performance for a wide range of applications, including power supplies, PFC (Power Factor Correction), DC-DC Converters, Plasma Display Panels (PDP), lighting ballasts, and motion control.
They offer reduced on-state loss by lowering on-resistance (RDS(on)), and reduced switching loss by lowering gate charge (Qg) and output capacitance (Coss). By using Advanced QFET® process technology, Fairchild can offer an improved figure of merit (FOM) over competing Planar MOSFET devices.
MOSFET Transistors, ON Semi
ON Semi offers a substantial portfolio of MOSFET devices that includes high-voltage (>250V) and low-voltage (<250V) types. The Advanced silicon technology provides smaller die sizes, which it is incorporated into multiple industry-standard and thermally-enhanced packages.
ON Semi MOSFETs provide superior design reliability from reduced voltage spikes and overshoot, to lower junction capacitance and reverse recovery charge, to elimination of additional external components to keep systems up and running longer.
Liens connexes
- onsemi QFET P-Channel MOSFET 100 V, 3-Pin TO-220AB FQP17P10
- onsemi QFET Type P-Channel P-Channel QFET MOSFET 500 V Enhancement, 3-Pin TO-220AB FQP3P50
- onsemi QFET N-Channel MOSFET 400 V, 3-Pin TO-220AB FQP6N40C
- onsemi QFET N-Channel MOSFET 60 V, 3-Pin TO-220AB FQP20N06
- onsemi QFET N-Channel MOSFET 400 V, 3-Pin TO-220AB FQP17N40
- onsemi QFET N-Channel MOSFET 60 V, 3-Pin TO-220AB FQP30N06
- onsemi QFET Type N-Channel MOSFET 300 V Enhancement, 3-Pin TO-220AB FQP22N30
- onsemi QFET Type N-Channel Power MOSFET 60 V Enhancement, 3-Pin TO-220AB FQP30N06
